

A diamond's color grade actually refers to the absence of color. In other words,
diamonds that are white, containing little or no color, receive higher quality grades than those with
noticeable color.
A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond has no hue, like a drop of
pure water, and consequently, a higher value.
A color scale established by the Gemological
Institute of America (GIA) assigns a letter to the degree of colorlessness found in a diamond. Beginning
with D and ending with Z, each descending letter denotes an increasing amount of light yellow, brown or gray
in the diamonds.
Color of the polished diamonds starts from Colorless D-F), near colorless (G-J),
faint color (K-M), very light color (N-R), light color (S-Z) to fancy color (Z+). In diamond trade
terminology is referred in alphabet starts from D to Z.
Clarity is basically inclusions in diamonds. Clarity can be categorized as
following, Flawless (FL), internal flawless (IF), very very slight inclusions (VVS), very slight
inclusions (VS) , slight inclusions (SI) and lowest clarity scale id Inclusion (I).
It is near
to impossible to have a diamond without impurities. Diamonds without inclusions or blemishes are rare.
Often invisible to the naked eye, these natural blemishes are categorized as — inclusions, which are
internal, and blemishes, which are external. When the stone was being formed sometimes trace elements or
minerals get trapped that result in inclusions that appear as feathers, clouds or crystals. Scratches and
chips visible to the naked eye are known as blemishes.
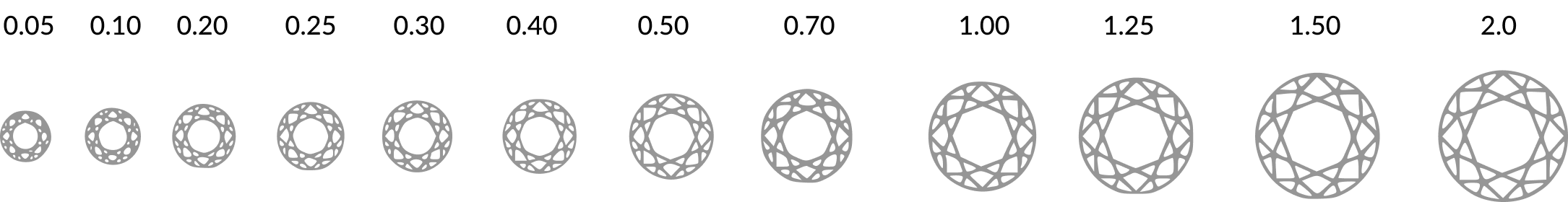
Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. A metric
"carat" is defined as 200 milligrams. Each carat can be subdivided into 100 'points.' This
allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place.
Carat reflects the weight of the
stone, which includes depth, height and diameter of the stones. Prior to the twentieth century, diamonds were
measured using carob seeds, which were small and uniform and served as a perfect counter weight to the
diamond. The word "carob” is the origin of the word "carat" that we use today.
One
carat is the equivalent of 0.2 grams One carat is also divided into 100 points. Points are generally used to
describe increments of weight within a carat. The weight of a 3/4-carat diamond can be shown as .75 carats or
75 points.
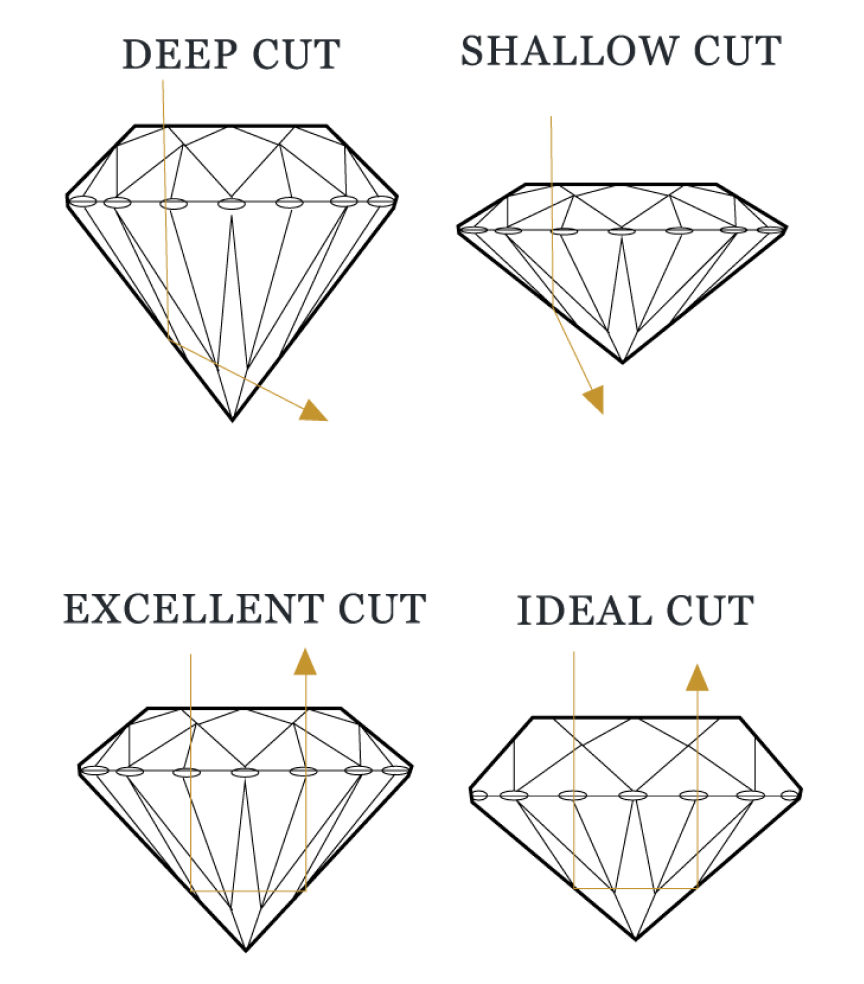
A diamond's CUT not only refers to its shape, but also how effectively the stone can return light back to the viewer's eye. A well-cut diamond will appear very brilliant and fiery, while a poorly cut stone can appear dark and lifeless. CUT verification can be done through comparison of parameters of facets. A well cut diamond will be symmetrically round, proper depth and width, and have uniformity of the facets.